-
A command line program for creating synthetic observations of galaxies from Illustris.
-
Create mock observations from Hubble Space Telescope, Sloan Digital Sky Survey, or James Webb Space Telescope.
-
Customize parameters like redshift, camera, filter etc…
-
Download SDSS backgrounds from here
This program was created by updating, compiling, and modifying the Sunpy Module by Dr. Torrey & Dr. Snyder. Unix/MacOS/Linux requirement
Installation
Dependencies required: numpy, matplotlib, astropy, cosmocalc, scipy, gc, and wget.
Downloading the repository
Clicking the ‘Download .zip’ or ‘Download .tar.gz’ will download a complete directory of files. However, this program has many dependencies, so the file called ‘setup’ should be run first.
If the files setup or Illustris Virtual Observatory are NOT executable- the following command will give them this ability:
u@urcomputer$ chmod +x setup; chmod +x Illustris \Virtual \Observatory
It may be beneficial for some to navigate to the directory containing these files through your terminal and executing them with:
u@urcomputer$ ./setup
...
u@urcomputer$ ./Illustris \Virtual \Observatory
This will ensure that all outputs are sent to the directory you are currently in & create environments in one terminal.
The file is written in bash and can be modified in a text editor before execution if manual dependency setup is preferred.
This will download any dependency that the program requires as well as open up a webpage to the Illustris Galaxy Observatory- where mock galaxies from the Illustris simulation can be viewed.
Choose A Sample
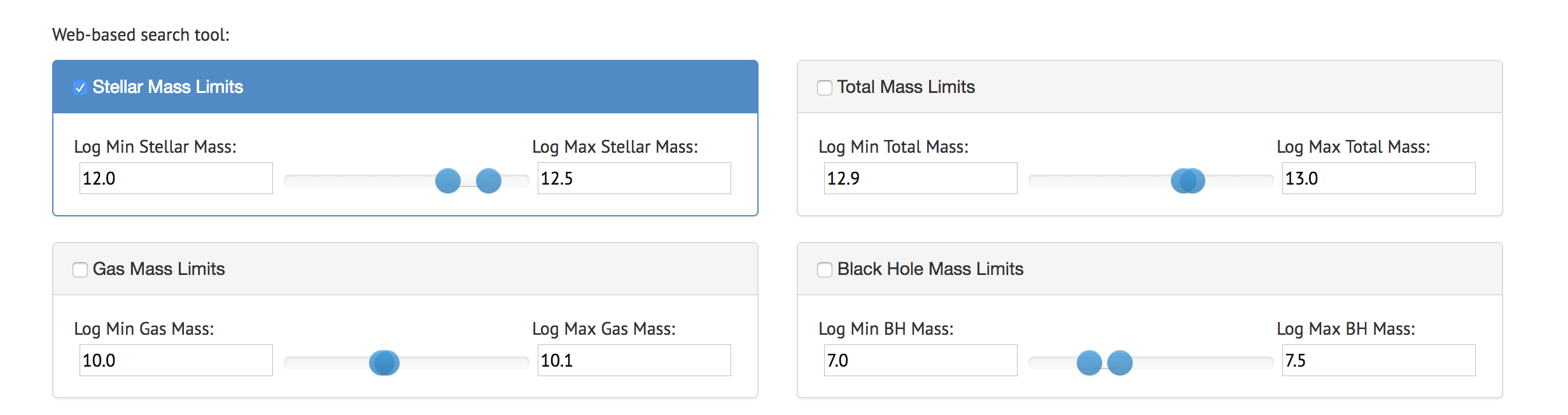
Use the search tool and narrow your catalog by varying mass limit contributions.
Search tools include: stellar mass limits, black hole mass limits, gas mass limits, and total mass limits.
Identify the galaxy ID
The ID for a given galaxy can be found to the left of its image. This ID will later be used to specify which galaxy you’d like for simulated observations.
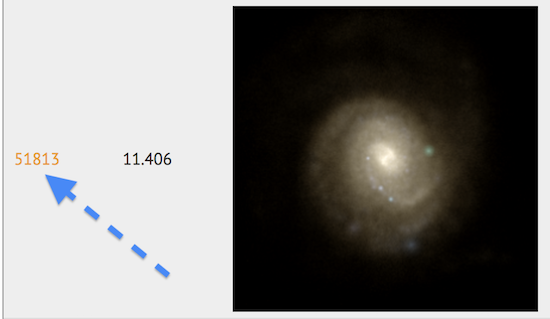
Once the ID number to the corresponding galaxy is found, make sure to save it somewhere for later!
Running the program
Make sure you’ve run the setup file and have all required dependencies installed…
Run the program titled Illustris Virtual Observatory- this should open up the following terminal window:
If the program doesn’t execute, first see if the shebang (#!/bin/usr/env python) (on the first line) is correct for your installation of Python. If you use anaconda or microconda, the shebang may have to be edited to point to the correct build of Python.
Follow the program and enter your chosen galaxy ID when prompted. If everything is working correctly, you should be given a choice:
-
Hubble Space Telescope (option 1)
-
Sloan Digital Sky Survey (option 2)
Based on your choice, the images produced will be convolved to the respective pixel-scaling/resolution.
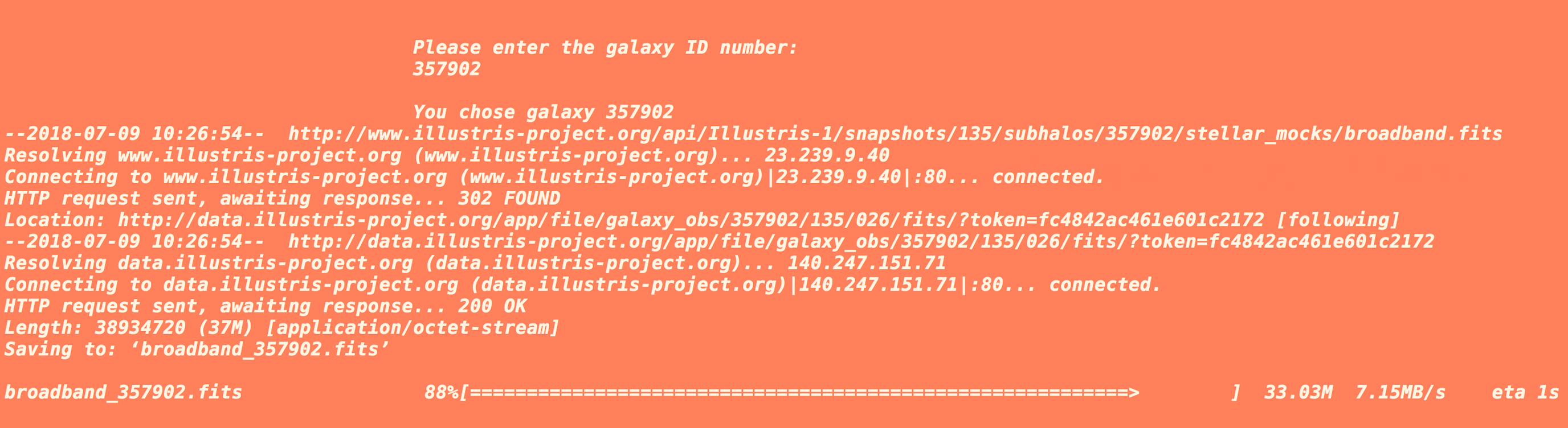
After selecting an instrument, the program should inform you when it has finished (and if it was successful).
Note: backgrounds are currently only available for SDSS. Basics on modifying the code are included in the next section.
The images you produced should now exist in the same directory that the program is in. Illustris Virtual Observatory should output .png and .fits files containing your observations.
Changing the program
The program file “Illustris Virtual Observatory” is a Unix executable- but it is written in Python 3. This means you can simply open the file in a text editor and modify the script to your liking.
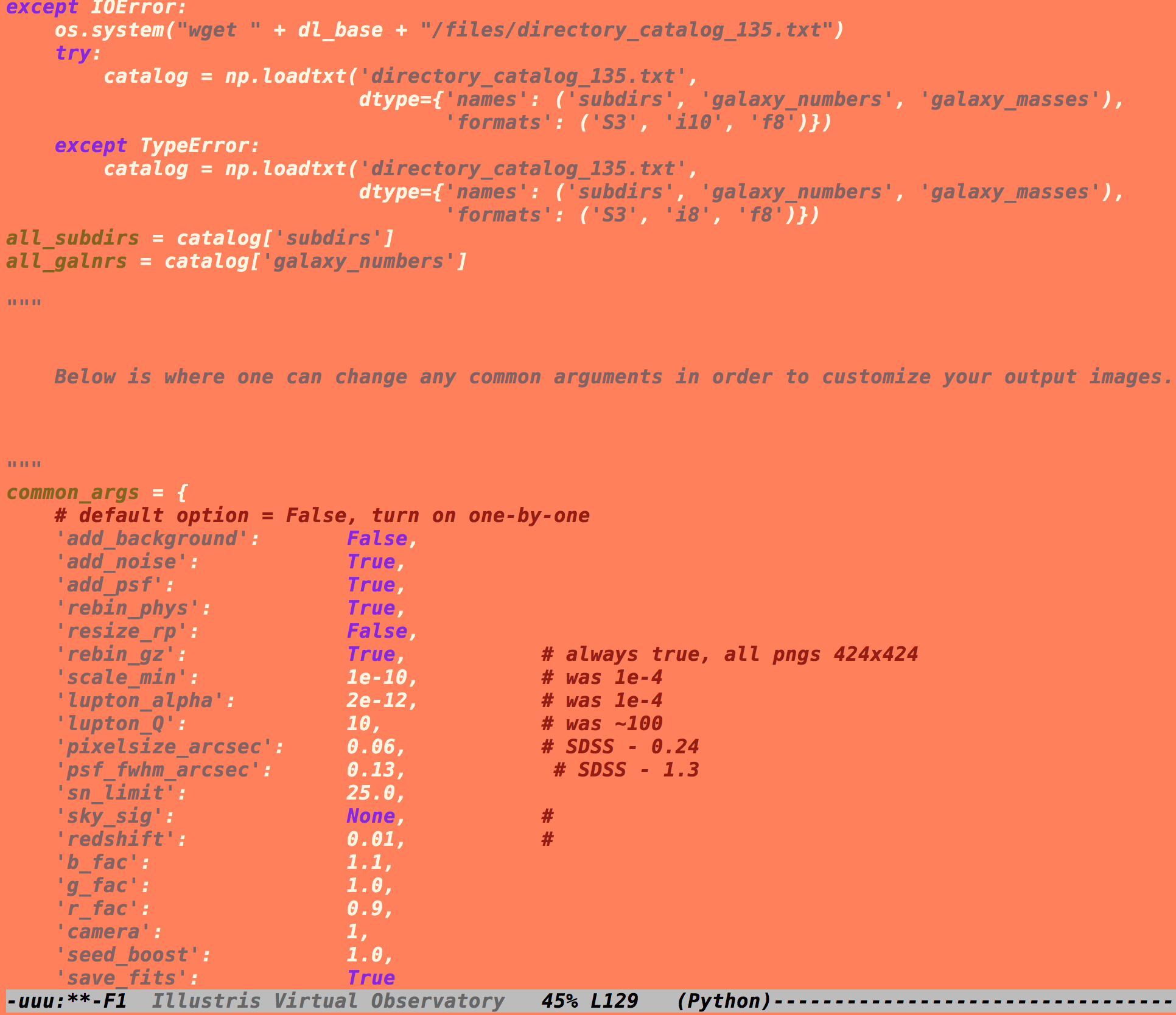
Here, you can completely customize the output. Changing the redshift on this page will make the image convolve to the corresponding value once the program is run. The file can also be modified to include multiple outputs, backgrounds, etc…
For more on modification, refer to the Sunpy module (source code).
Tyler Metivier, Whitaker Research Group, University of Connecticut
funded by NASA CT Space Grant Consortium through an Undergraduate Research Fellowship Grant
